- Home›
- Healthy Living›
- 10 Things That Sugar Does To Your Body
10 Things That Sugar Does To Your Body
By: Jhanvi Gupta Thu, 08 May 2025 11:38:13

You’re probably aware that a candy bar or a can of soda isn’t the healthiest option, but you might not fully realize how their sugar content impacts your body. In this article, we'll explore the harmful effects of sugar on your health.
Processed sugar is the white granules you add to your coffee, tea, or baked goods. It’s also found in everyday foods like processed snacks, canned goods, and sodas. Sugary foods and drinks are high in calories, contributing to weight gain.
Sugar-sweetened beverages, particularly sodas, offer no nutritional value and contribute to weight gain. This increases the risk of diabetes, bone fractures, and dental issues. When consumed in excess, sugar is converted into fatty acids and stored in adipose (fat) cells, which accumulate in areas like the hips, thighs, arms, and stomach.
The World Health Organization recommends consuming less than 25 grams of sugar (about 6 teaspoons) daily for overall health. Did you know that a can of soda contains roughly 38 grams of sugar?
Here are some of the scary ways sugar affects your body:
# Sugar Spikes Your Insulin
Excess sugar causes a spike in insulin levels, which helps regulate blood sugar. Soda is particularly harmful because its sugar is absorbed rapidly, causing a quick rise in blood glucose and insulin. On the other hand, natural sugars from fruits don’t have this effect, as they’re paired with fiber, which slows absorption.
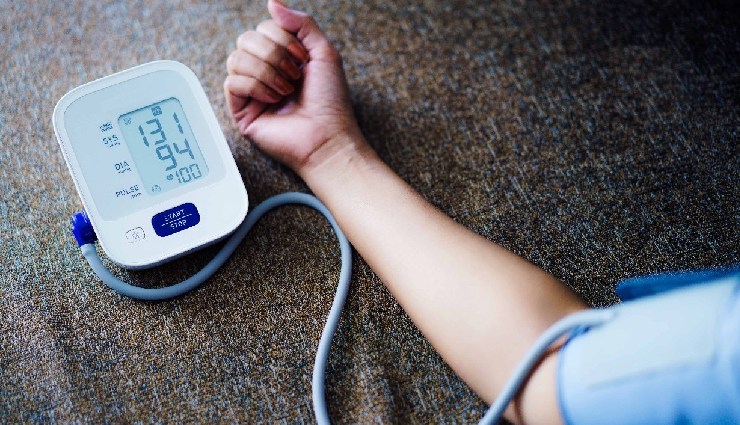
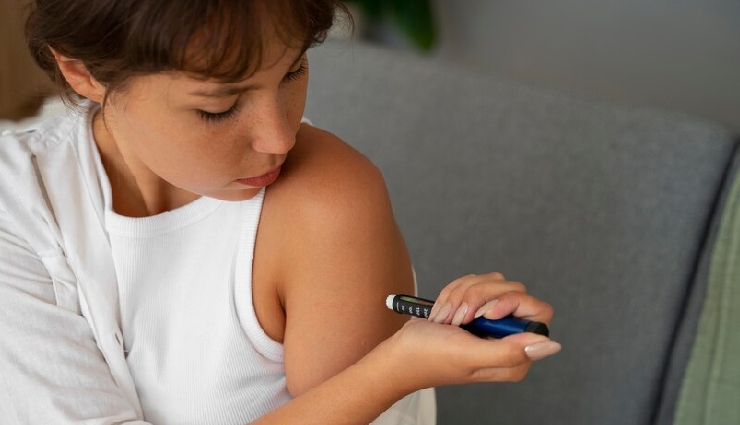
# Sugar Increases the Risk of Diabetes
When the body becomes resistant to insulin, the pancreas must produce more of it. This can eventually exhaust the pancreas, leading to an insufficient supply of insulin and potentially resulting in type 2 diabetes. For diabetic adults, the recommended daily sugar intake is 22 grams for women and 36 grams for men.
# Sugar Contributes to Weight Gain
The body needs some sugar for energy, but excess sugar is stored as fat. Studies have shown that added sugars contribute to weight gain and obesity, which in turn increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. Added sugar is also linked to increased waist circumference, raising the risk of heart disease.
# Sugar Raises Blood Pressure
Research indicates that sugar consumption is associated with high cholesterol and heart disease. Excess sugar can increase very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) levels, which boosts the risk of cardiovascular diseases. It can also lead to hypertension by affecting the kidneys and arteries, causing blood pressure to rise.

# Sugar Disrupts Brain Signals
Too much sugar can impact brain function. Energy-dense, sweet foods may trigger reward systems in the brain, reinforcing cravings for sugary foods. Sugar activates pleasure centers in the brain, similar to how drugs do, making it harder to resist.
# Sugar Can Leave You Feeling Hungry
Since sugar provides no nutrients, it doesn’t satisfy your hunger. Sugary liquids, in particular, aren’t satiating, as people don’t often account for the calories they consume in liquid form. This can lead to overeating and a higher total calorie intake.
# Sugar Can Lead to Fatty Liver Disease
Fructose, a type of sugar, is metabolized in the liver. Excessive sugar intake can increase fat production in the liver, which may lead to fatty liver disease. People who consume too much sugar are at higher risk of developing this condition.

# Sugar Causes Inflammation
Excess sugar is a major cause of inflammation in the body, which can trigger chronic diseases and lead to aches and pains. When blood glucose levels crash after a sugar high, inflammation occurs in joints and blood vessels. Reducing sugar intake may help individuals with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
# Sugar Contributes to Leaky Gut
Sugar alters the gut microbiota, which can lead to leaky gut syndrome. Symptoms include allergies, eczema, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Sugar feeds harmful bacteria and yeast in the gut, damaging the intestinal wall and causing a leaky gut.
# Sugar Increases the Risk of Depression
High sugar levels from simple carbohydrates cause blood glucose levels to spike and crash, which can worsen your mood and lead to irritability, agitation, and poor sleep. These fluctuations can also increase inflammation. For better mental health, replace sugary foods with lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and omega-3-rich foods.





